This is a collaborative space. In order to contribute, send an email to maximilien.chaumon@icm-institute.org
On any page, type the letter L on your keyboard to add a "Label" to the page, which will make search easier.
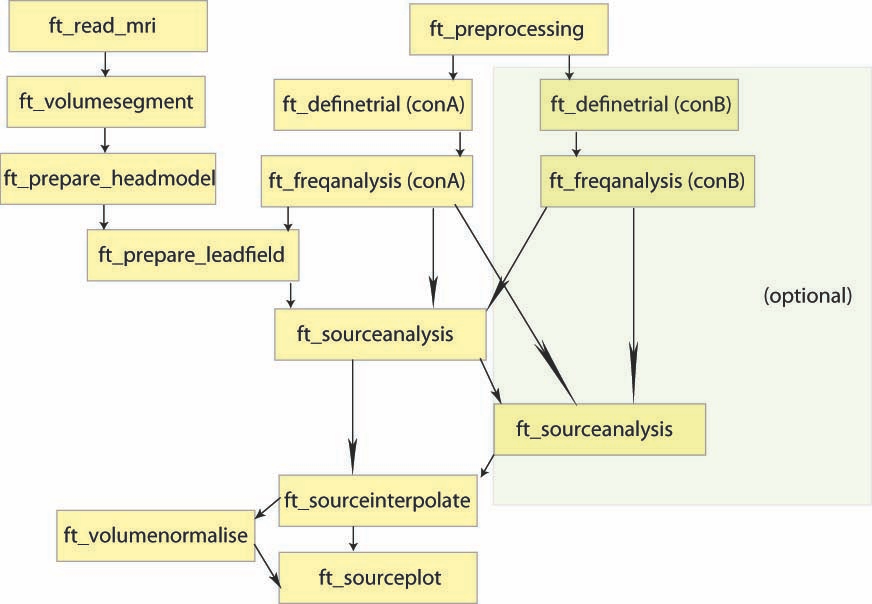
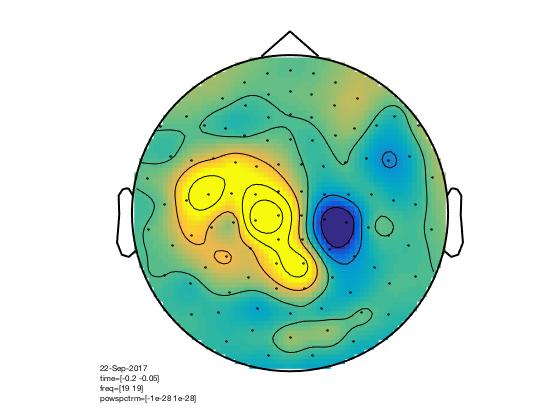
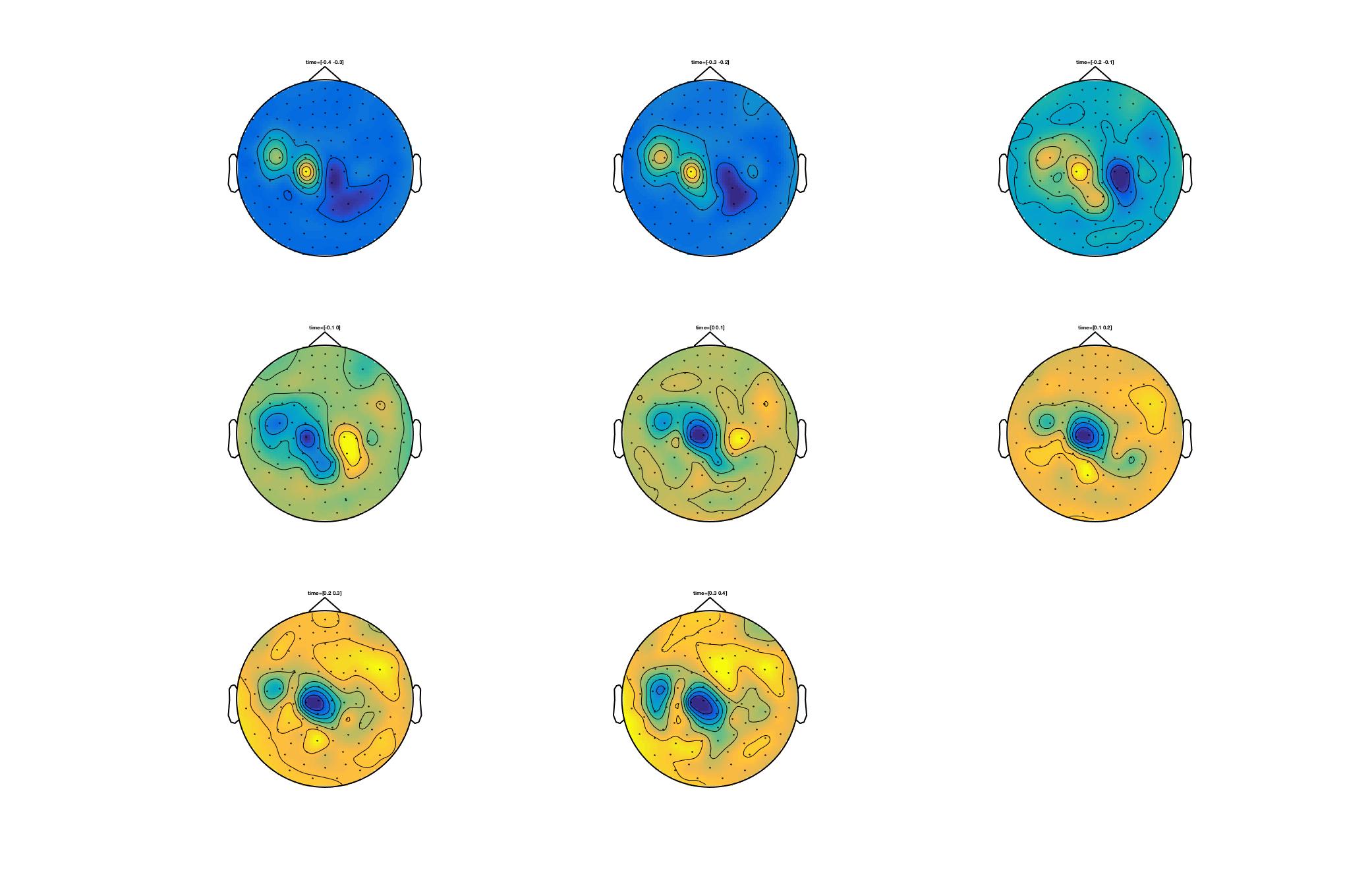
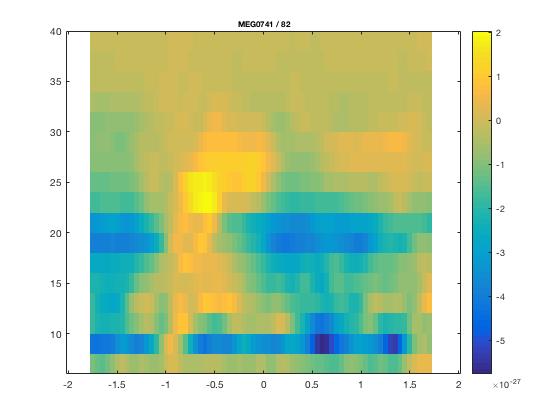
Single trials - Sources analysis
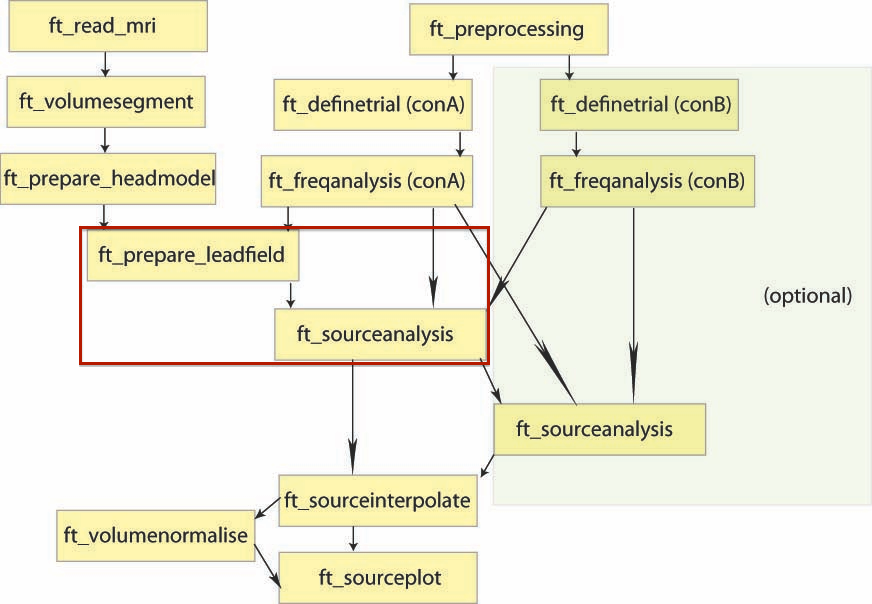
In this tutorial, you will find a description of all the steps necessary to obtain sources localisation of continuous (non averaged) data using a D.I.C.S beamformer approach in FieldTrip for one subject.
Prerequisites
- Read the previous tutorials (MEG EEG pre-processing, MEG sensors realignment, filter, baseline correction)
- Pre process the T1 MRI data or choose a template
- Download the latest version of FieldTrip - Install it in your software folder - Take a look at the FieldTrip tutorials!
Input data
MEG signals (MEG)
FieldTrip can import the fif files coming from our MEG system and those pre processed with our in-house tools. If you acquired simultaneous MEG+EEG data, FieldTrip will import both of them.
MRI
If you have the individual anatomy of each of your subjects (T1 MRI), you should process it with FieldTrip as described below.
If you don't have the individual anatomy, then you have to choose a template in FieldTrip.
Needed software
For MEG fif files pre processed outside FieldTrip: You will need two in-house scripts to read the marker files we add to the MEG fif files (put them in your matlab path):
A short script to pre process the MRI in FieldTrip: pre_process_mri_for_ft.m
A simple script to visualize beamformer results: visuBF.m
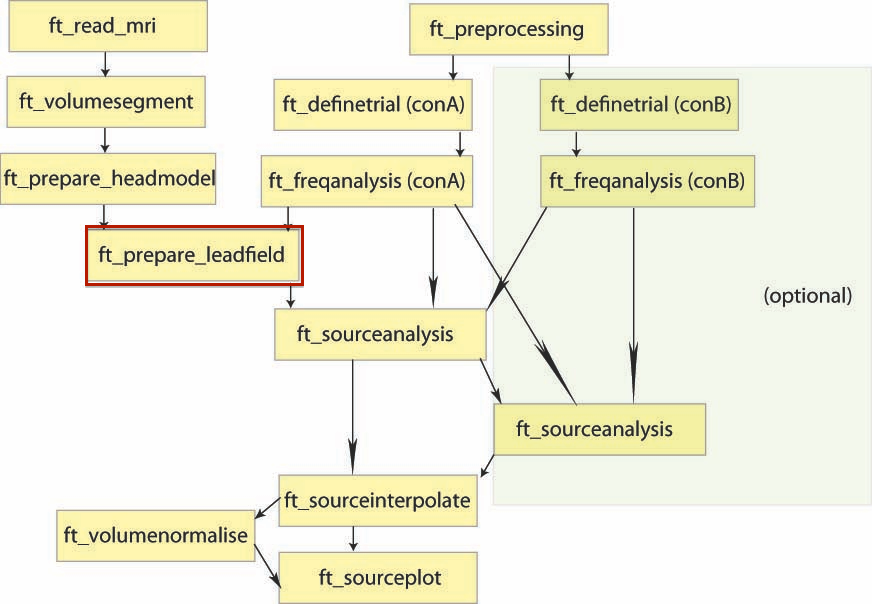
D.I.C.S. analysis with FieldTrip
Overview of the process: